IP address location – how it works
IP address location works by establishing a link between a user IP address and its geographical location. The location (also known as Geo IP location) generally applies to a range of IPs rather than each individual IP. Therefore, there is always a measure of privacy when an IP address geo location is detected. Let’s discuss the methods being involved in detection of Internet Protocol address location.
There are two primary methods of getting an IP address location
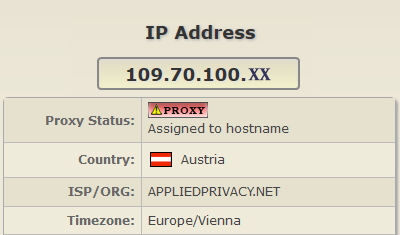
When a computer that’s connected to Internet is assigned a Wide Area Network (WAN) IP address, the location data of that IP is gathered from either one of the following sources
- IP address IP-to-location computer database
- ISP and website hosting providers’ internal IP address location database
Each source of the geographical location data has its own advantages and a purpose of utilization. They are not interchangeable since the precision and the data privacy aspects play a role on a case basis.
In this article we will provide basics about each IP location data source and their common use.
1. IP-to-location (Geo IP) computer database
This is the most commonly utilized source of an IP address location information. It is used in about 98% of all web applications and hardware devices that use connecting device geolocation for various purposes.
📈 Sign Up now to instantly track website visitors IPs!
The Geo IP location databases can be either embedded into the device software or remotely hosted by a third-party server. For web applications that need a high speed of IP data to be gathered, the databases of this type are generally hosted and embedded into the web application itself.
One of the examples of Geo IP database usage is website statistics services such as provided by TraceMyIP. It allows its users to see the general location of visitors who come for information to their websites. It provides a useful resource for webmasters to understand the impact and geographical coverage that their websites provide to their visitors. It also helps to determine if web publishers’ marketing efforts work for the geo-locations that are most important to them.
Although the Geo IP databases are utilized in the majority of situations, there are a few things to note about their limitations
- The IP location that comes from bulk IP information databases does not provide an exact location of each IP address but rather provides an approximate location area of an IP range to which a particular address belongs. Therefore, this data cannot be used to determine a connecting device street address for example.
- Some databases are more precise than others and therefore not all services that use Geo IP databases provide the same level of precision. This is because the most accurate databases can be cost-prohibitive to utilize for a small online business. Some moderate precision IP databases for example are updated monthly and can cost thousands of dollars a month.
- Most commonly, device IPs are dynamic by nature, meaning each Internet connection can change its IP assignment from time to time. Mobile devices, for example, change their IP address each time a different cell phone tower is connected to a device. It makes it more complex to track a specific device by an IP address since its IP address is frequently altered.
- The data that is compiled into an IP database has many different sources, and each source has its own privacy policy that mostly prohibits disclosure of the exact location of a device user.
- Geo IP databases do not compile a location for each IP address individually. Instead a range of IP addresses is grouped into a block with a location assignment. This is done to reduce the size of a database, which otherwise could scale to terabytes if each IP had its own data block. Even though the size of a database could be managed, searching such database for each IP query would take so much time and CPU power that it would become very inefficient in scope of high performance web applications.
The most common database sources of Geo IP data
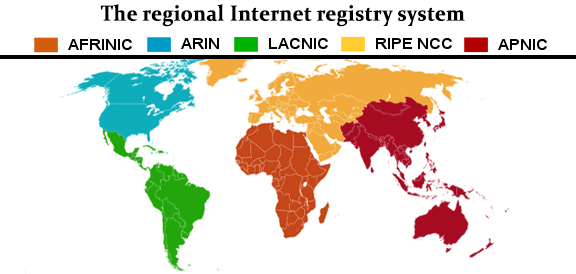
The main sources of IP location data are the regional Internet data registrars. These distribute and allocate IPs to organizations positioned in their associated service regions. These include but not limited to:
- RIPE Network Coordination Centre (RIPE NCC)
- American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN)
- Latin American and Caribbean Internet Address Registry (LACNIC)
- African Network Information Centre (AfriNIC)
- Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC)
Other additional sources that can be used for an IP address database compilation are:
- ISP providers
- Web hosting data centers
- Local area civilian service provider websites that gather IP addresses of people actively for applicable services based on specific address location
- Human resources agencies that register its own user group and collect IPs which are later associated with specific individuals
- Bank and energy/supply utility companies which capture user IP addresses through their online gateways
- Data mining organizations such as weather forecasting websites that can associate IP addresses accessing region specific forecasts.
- Government agencies that provide online services to their citizens
2. ISP and website hosting providers’ internal IP address databases
This type of IP location sources are the most accurate, and depending on the requesting agency, they can pinpoint an IP address location to an exact street address and the actual individual or an organization that utilizes it, including the full history of utilization and IPs used in the past.
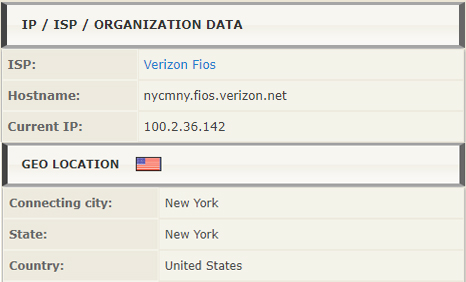
The advantages and disadvantages of acquiring information from ISP provides and web server hosting companies directly are:
- The data that discloses individuals or a specific property is not easily accessible, generally not in real-time and requires proper clearances and paperwork
- This method is mostly used for legal enforcement or internal uses that manage service subscribers
- There are no IP location databases with this informational accuracy that’s available in bulk to any third party consumers. The data release is generally managed on a case by case basis.
Both methods of IP location data acquisition have its purpose, definition of usage and accessibility. IP addresses cannot be closely compared to phone number since they are interchangeable. This means that even if someone captures your IP address, there is a little privacy concern because:
- The IP location that’s available to third parties is not exact, and your IP address will eventually change, unlike a phone number that is generally utilized for extended periods of time as a point of contact. The IP addresses are not used as a point of contact for Internet access by individuals or organization.
- If you are connected to Internet through a router with a firewall, a direct link between an external device cannot be easily established with your device in order to access a data on your Internet connected device unless there’s a malware or another method of data reach is present.
One of the most common uses for acquiring an exact location of an IP address that’s connected to an event that breaches a law is crime investigation. When a crime is committed using a network connected device which IP address has been linked to this type of activity, the legal authorities immediately issue a warrant on personal information release. The warrant is served to an ISP provider or a web server hosting agency that provides the requested personal data information to assist in the legal proceedings.
It is also worth to mention that there is another way of getting a User IP location, which is HTML5 geolocation API that produces sufficiently accurate results. It approximates the location based on a number of factors including the public IP address, device GPS information, cell tower data, a list of known Wifi access points and their signal strengths. However, unlike the database driven location data, HTML5 API requires an Internet user to provide an interactive consent before this method could be used. This renders it ineffective for the purpose of passive location acquisition and thus is not suitable for most purposes as discussed above.
🌍 Who visits your website? Sign Up now to find out instantly!